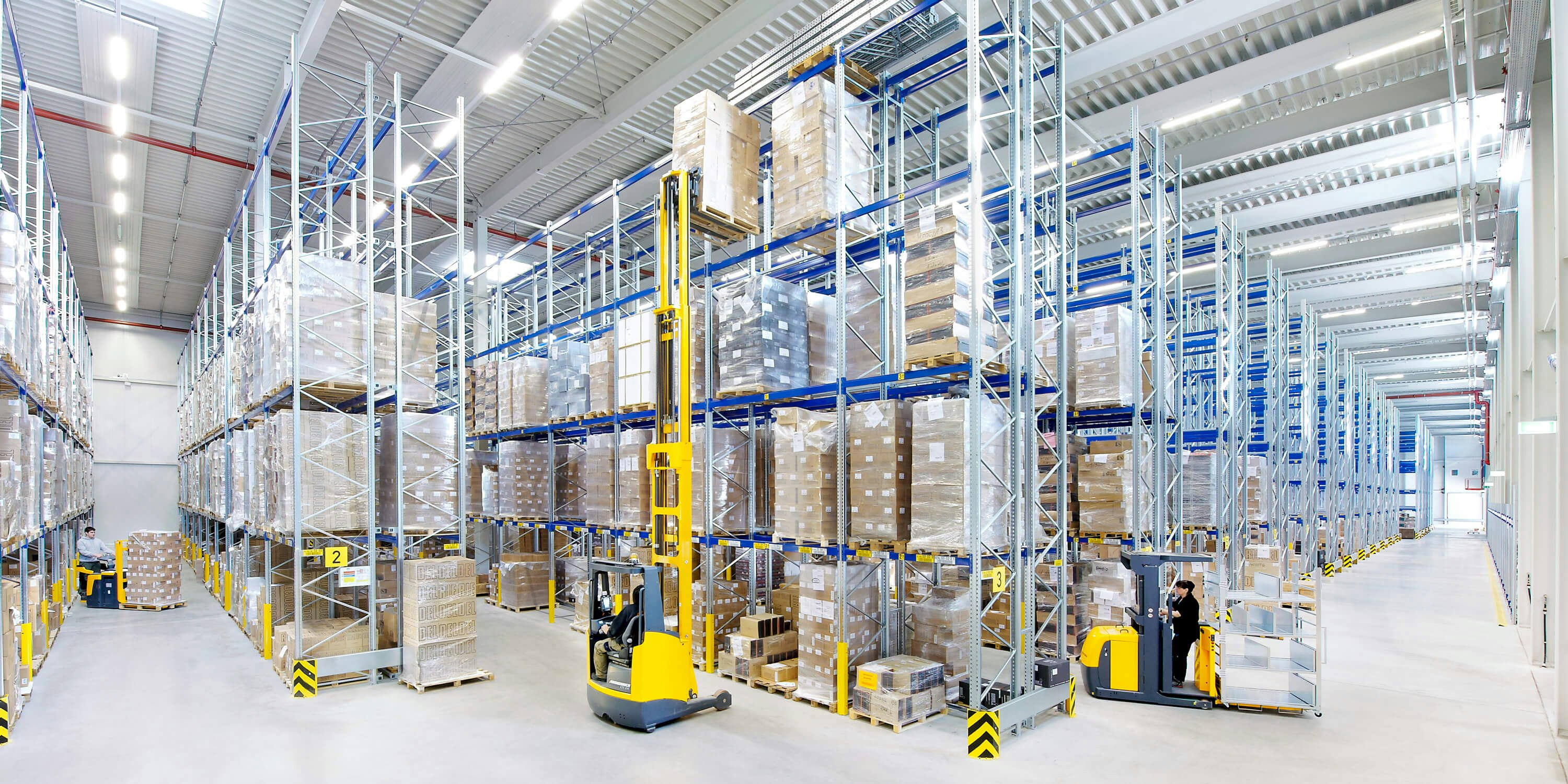
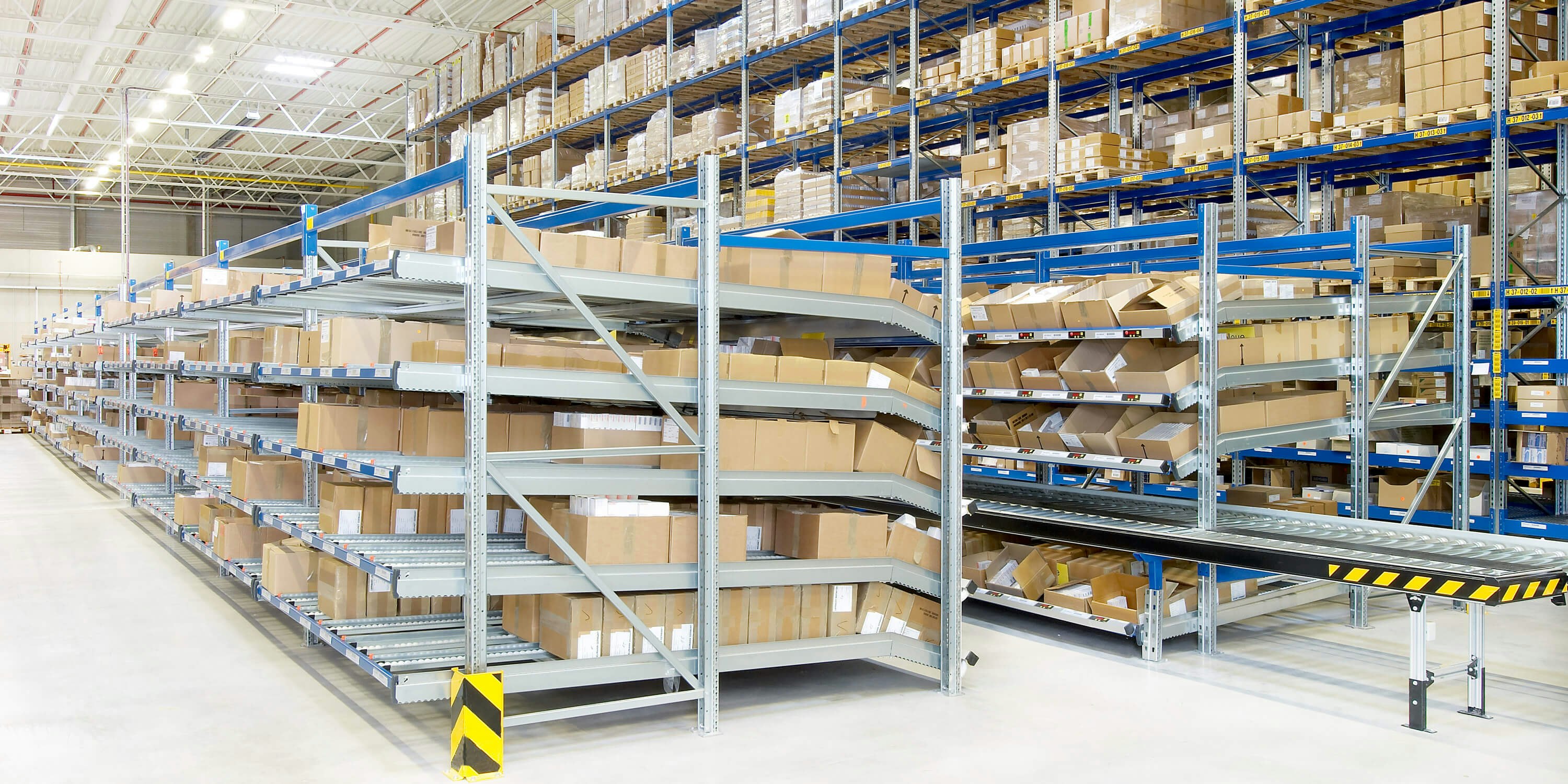
Warehouse order picking

Every day, customers order goods online or offline that need to be retrieved from the warehouse and made ready for shipment by order pickers to fulfil the order. The items to pick are transmitted in the form of paper or electronic pick lists to the corresponding picker.
The nature of the goods and the warehouse determine the type of order picking
The type of warehouse or goods determine the type of picking to use. The FIFO (First In, First Out) procedure means that the goods stored first are picked first and removed from storage. This means that newly arrived goods are stored at the rear and the goods to be retrieved first are stored at the front of the racking. The FEFO (First Expired, First Out) procedure is used when a product has a best-before date and must therefore be picked first. If a longer storage period has no influence on the quality of the goods, such as metal products or certain bulk materials the LIFO (Last In First Out) principle is applied.
1. Goods-to-man picking
With Goods-to-man picking the goods are brought directly to the order picker by means of conveyor technology. The order picker then accepts the goods at the picking station and removes the quantity specified by the warehouse management system. The empty containers or containers filled with residual quantities are then transported back to the warehouse using the same conveyor.
Vorteile
- hohe Kommissionierleistung durch Einsparung von Wegzeiten
- hohes Artikelspektrum möglich
- geringe Fehleranfälligkeit
- Behälter werden leicht und automatisch zurück transportiert
- Aufbau eines ergonomischer Arbeitsplatzes möglich
Nachteile
- Relativ hohe Investitionskosten für automatisierte Regal- und Entnahmesysteme
- weniger Flexibilität durch feste Anzahl von Kommissionierplätzen
- Bei Maschinenausfall kann es zum Lagerstillstand kommen
- keine Flexibilität für den Kommissionierer bei schwankenden Anforderungen
Examples of goods to man picking equipment include: carousels, vertical storage racks, tower racking, automatic picking storage system, flow racking with automatic conveyors and high-bay racking with automatic rack conveyors.
2. Man-to-goods picking
With Man-to-goods picking the order picker goes to the storage location and removes the required goods. This type of picking is therefore particularly suitable for smaller orders and goods of low weight. If multi-stage picking is used (see below), this picking method can also be operated economically in large distribution centres.
Vorteile
- geringer Investitionsaufwand nötig
- hohe Kommissionierleistung bei optimierten Kommissionierwegen möglich
Nachteile
- erhöhte Anstrengung bei der Warenentnahme
- längere Laufwege und Wegzeiten
- schwierige ergonomische Arbeitsplatzgestaltung
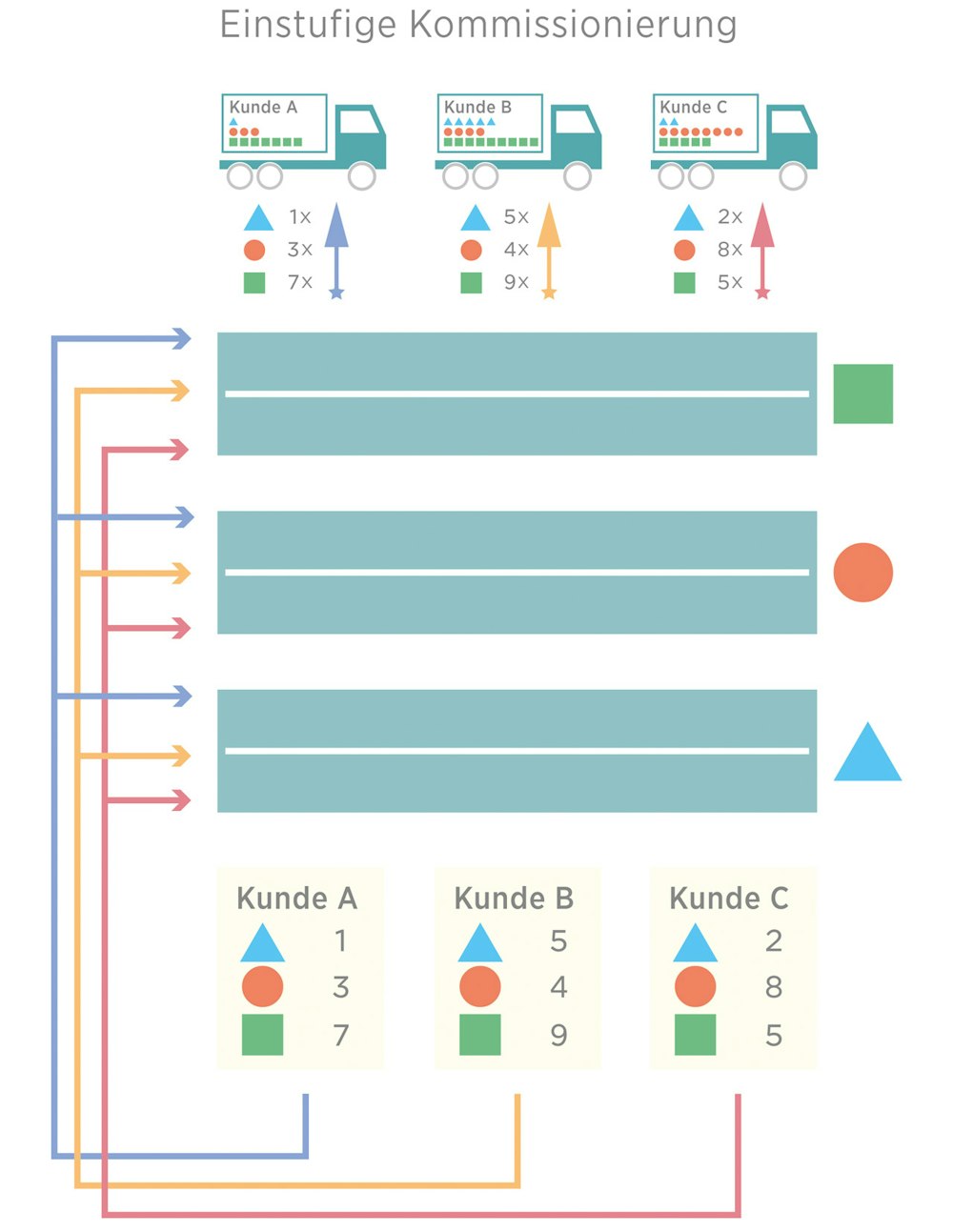
Single stage picking
With single stage picking, each customer order is compiled individually. Order-oriented parallel and order-oriented serial picking are used as picking methods. With parallel picking, an order is divided into different picking zones and processed simultaneously. Larger orders are divided and processed in different storage zones at the same time. As soon as all partial orders have been completed, they are consolidated again at a collection point to form the respective complete order. This leads to a saving of distances and a shorter processing time of the orders. However, a consolidation unit is required to combine the part orders. The entire process must be coordinated and controlled by a warehouse management system.
In serial picking, the items in the order are processed successively. Either an order picker passes through all warehouse zones or an order is transferred from one order picker of a certain zone to the next order picker and his zone – in a relay run – until all order positions are completed. The distances travelled are relatively small, as a picker moves in small picking zones. Since the order is not split but passed on, no consolidation is necessary. The disadvantage is that the orders have to be temporarily stored at the transfer points. This can also result in an unequal supply of order pickers with orders.
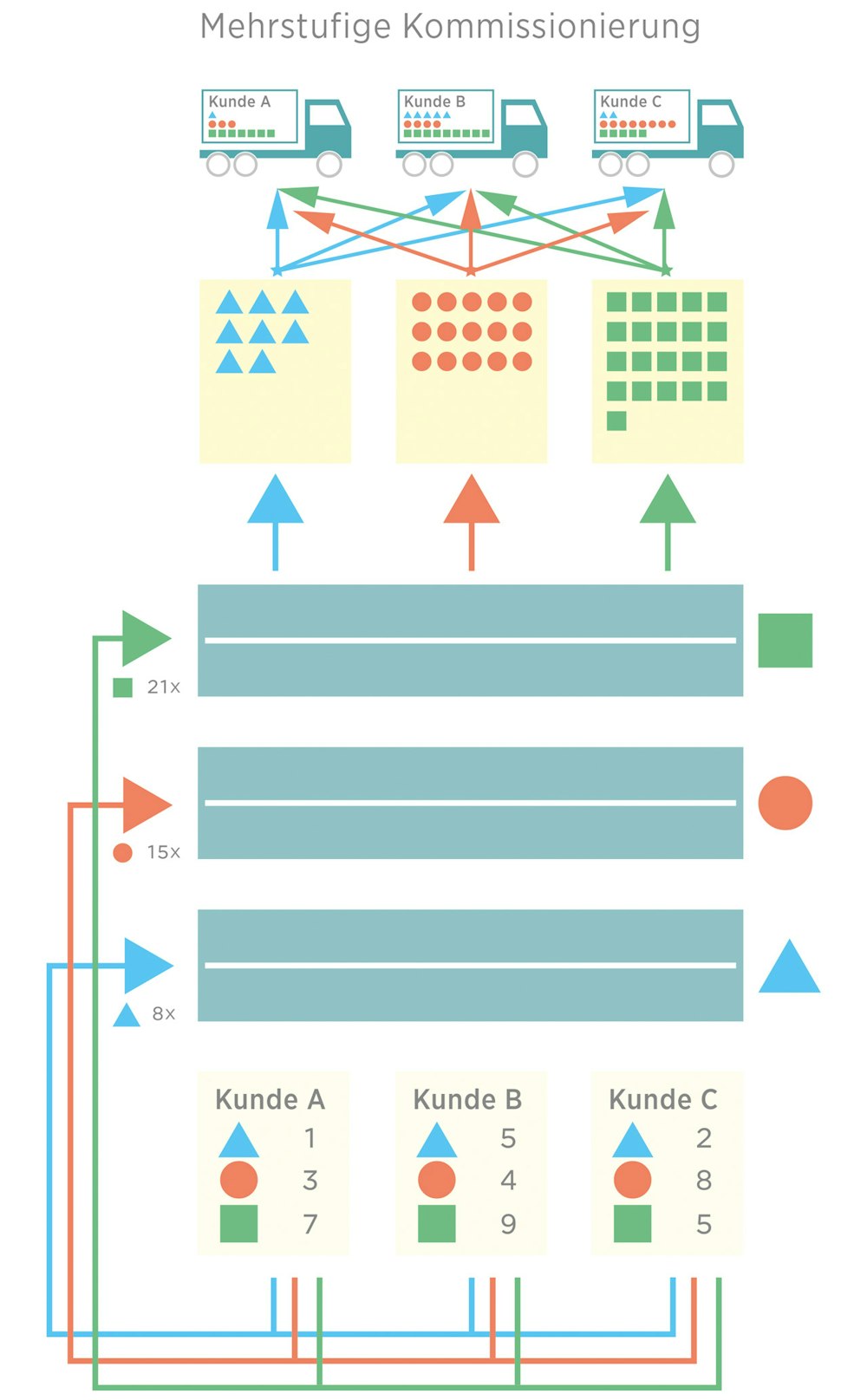
Two- stage or multi stage picking
With two-step picking, the entire quantity of an article can be picked simultaneously or in parallel for a large number of orders. The number of times a picking route and an article are accessed is drastically reduced (in the best case to just once). Several orders are bundled to a total order, then picked based on articles and packed later based on orders. The use of downstream sorting – using either a fully automatic or manual sorter – allows a far-reaching decoupling from the order reference during order picking. Two-stage picking is also called series-oriented, parallel picking. A major advantage is that the container frequencies in the individual storage areas are greatly reduced and the performance limits of the conveyor technology are less exploited. Two-step picking is suitable for operations such as mail order or pharmaceutical wholesalers.
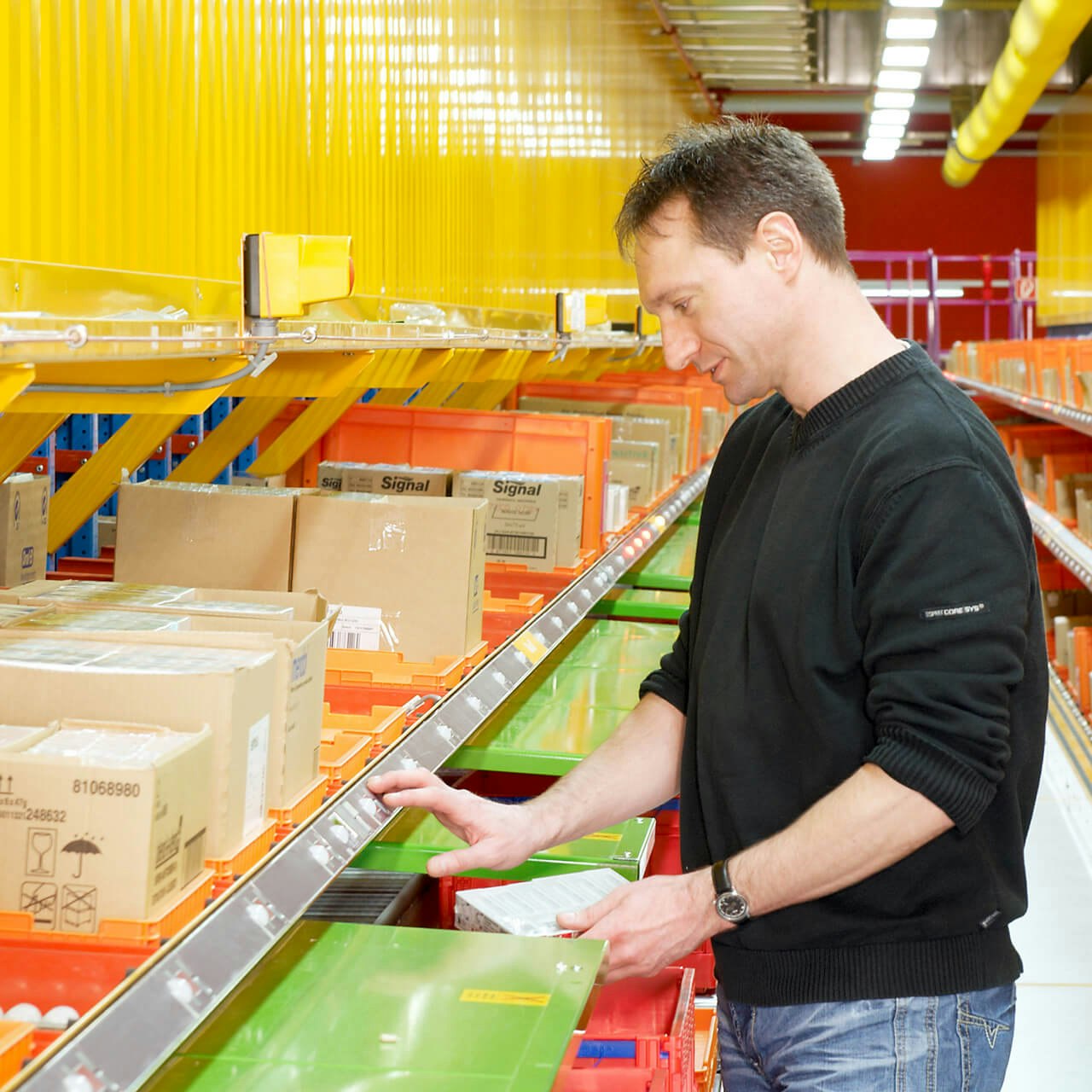

Pick-by-Light
Dies ist ein optisches, belegloses Kommissionierungsverfahren. Leicht lesbare Lichter, die direkt am Lagerplatz angebracht sind, zeigen an, wo die nächste Einheit kommissioniert werden soll. Ein Display gibt zusätzlich die Anzahl der Einheiten an, die gepickt werden müssen. Nach der Entnahme bestätigt der Kommissionierer den erfolgten Prozess durch Knopfdruck, und das Signal erlischt. Pick-by-Light wird für hohe Kommissioniergeschwindigkeiten bei niedriger Fehlerrate eingesetzt.
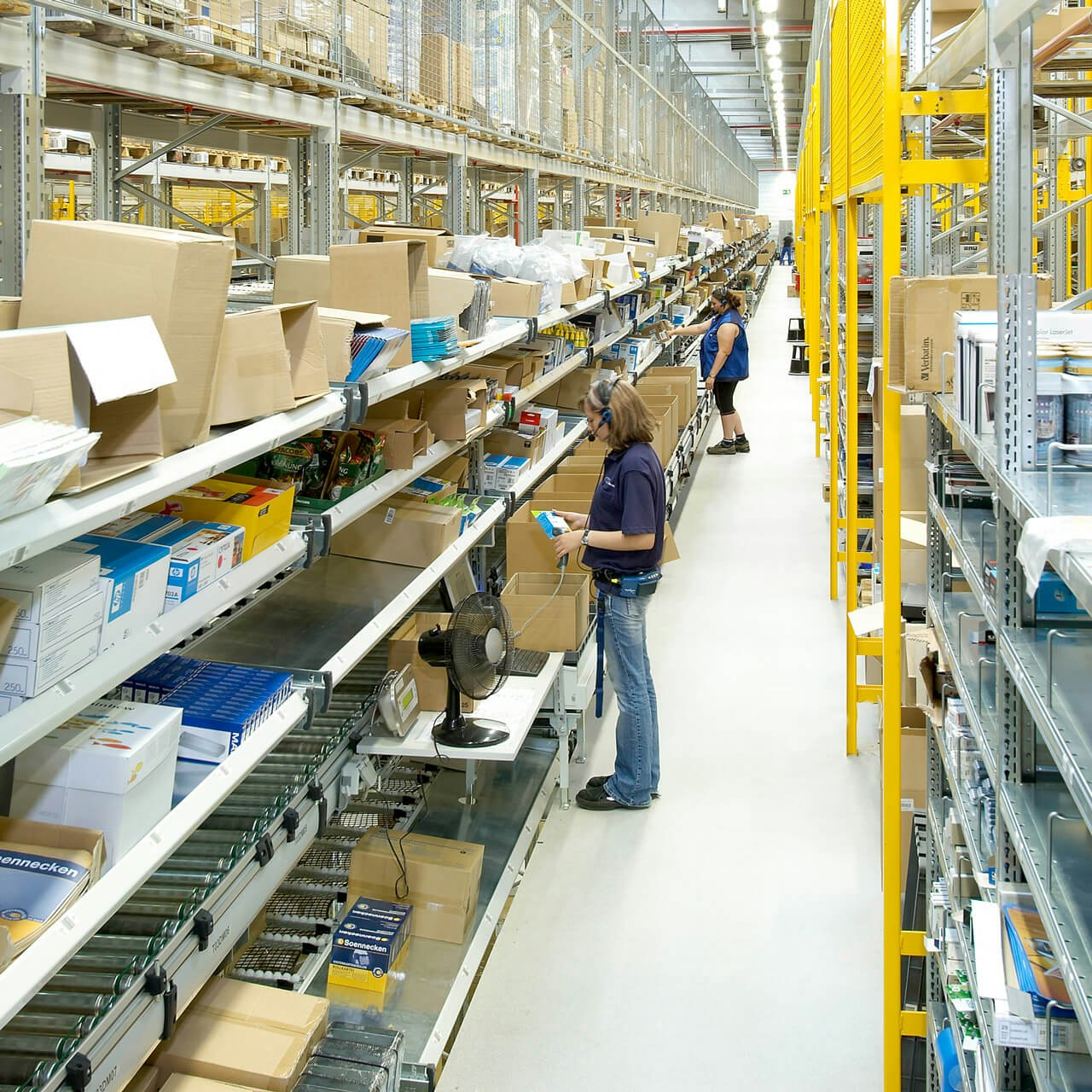

Pick-by-Voice
Dies ist ein sprachgestütztes, belegloses Kommissionierungsverfahren. Der Kommissionierer kann seine Hände freihalten und sich ungestört auf die Kommissionierung konzentrieren. Durch das Lagerverwaltungssystem (LVS) werden ihm die Aufträge über ein Voice-Client übermittelt und nach Quittierung direkt wieder an das LVS zurückgemeldet. Aufwändiges Suchen entfällt, Fehlerquoten werden reduziert und die Kommissionierleistung steigt.
Pick-by-Terminal
Die Datenübertragung erfolgt per Funk zu einem fest auf dem Flurförderzeug installiertem Terminal. Dieses Kommissionierverfahren setzen gerne Unternehmen ein, die überwiegend große und sperrige Güter handeln. Da die Bedienung des Terminals intuitiv erfolgt, entfällt das aufwändige Einlernen von Kommissionierern. Die Fehlerquote ist sehr niedrig, allerdings können Sprachbarrieren der Mitarbeiter zu Fehlerquellen werden.
Pick-by-MDE / Pick-by-Scan
Beim Pick-by-Scan bewegen sich Mitarbeiter mit mobilen oder Stapler-Terminals für die mobile Datenerfassung durch das Lager. Die Kommissionierliste wird den Mitarbeitern vom LVS direkt auf dem jeweiligen MDE-Gerät angezeigt. Die entnommenen Artikel werden auf dem Gerät bestätigt und auch Fehlmengen oder Nullmengen können eingegeben werden. Der aktuelle Status des Kommissioniervorgangs kann im LVS verfolgt werden. Vorteile sind z. B. geringere Suchzeit und weniger Pickfehler. Nachteile sind eine relativ hohe Anfangsinvestition (bis zu 2000 Euro pro MDE-Gerät) und die nicht handfreie Kommissionierung.

